Function Of Computer
Function of Computer have become an integral part of our daily lives. We rely on them for everything from communication to entertainment to work. But what exactly is the function of these machines? At their core, computers have a few key functions that enable them to be so useful.
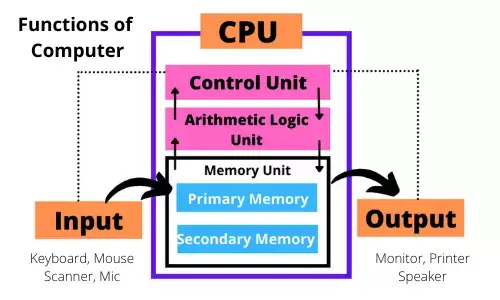
Basic Function of Computer
There are four basic functions that all computers perform:
1. Input
The input function refers to how information gets into the computer. Typical input devices include the keyboard, mouse, microphone, camera, and scanner. These allow users to enter data, select options, give commands, and more. Without input, a computer would just sit there without any purpose or utility.
2. Storage
Computers need to be able to store information for later use. This is accomplished through storage devices like the hard drive and solid-state drives. Information remains saved even when the power is turned off thanks to non-volatile storage. This function enables users to retrieve files, reuse data, and more.
3. Processing
The central processing unit (CPU) takes information from input devices and memory storage and processes it according to programmed instructions. This processing function is the “brain” of the computer, allowing it to perform all types of calculations, render graphics, run programs, and carry out user commands.
4. Output
Processed information gets sent to output devices so users can interact with it. Monitors, speakers, printers, and more make up a computer’s output function. This return of processed information completes the basic computer functions cycle.
Now let’s look at some specific input, output, storage, and processing devices and how they enable computers to be so functional.
Input Device Function of Computer
Input devices feed information into the computer for processing. They translate actions, commands, and data into a digital format the computer can work with. Common input devices serve various functions:
– Keyboard
The keyboard remains one of the primary input devices for desktop and laptop computers. The standard QWERTY layout allows users to input letters, numbers, and symbols through key presses. Special function keys enable quicker access to certain controls and operations. Keyboards facilitate typing, entering passwords, writing documents, coding programs, video game control, and more.
– Mouse
Moving a mouse on a flat surface translates that motion into movements of the cursor on-screen. Clicking the buttons enables selecting, opening, and interacting with all kinds of interface elements. Mice allow easier navigation through operating systems, programs, and files than using just a keyboard. Certain types of mice include extra buttons and controls for more functionality.
– Trackpad
Found on most modern laptops, trackpads function much like mice but use finger movement directly on the pad to control the cursor. Multi-touch trackpads even facilitate various finger gestures for zooming, scrolling, accessing extra options, and more. Built right into the chassis, trackpads enable cursor control without needing an external mouse.
– Microphone
A microphone allows audio input into a computer. Voice recognition software can interpret speech for writing, commands, or translations. Recording audio through a microphone enables podcasts, music, videos, voiceovers, and more. Special mics can also input other sounds like instruments or ambient noise.
– Camera
Video cameras serve as “eyes” for the computer, enabling visual input. Live footage facilitates video calls and conferences. Captured images and videos can be saved and edited in creative projects. Camera inputs allow uses like facial recognition, gestures, augmented reality applications, photography, and much more.
– Scanner
A scanner digitizes physical documents, images, objects, and more into a digital format. This facilitates saving and editing files as well as text recognition. Artists can scan sketches, photographers can digitize film, and users can upload important documents. Scanned inputs greatly expand computers’ ability to work with physical media.
– Touchscreen
Touchscreens allow direct finger-based interaction with the computer interface. Smartphones, tablets, interactive kiosks, and more use touch inputs instead of mice or keyboards. Gestures like taps, swipes, drags, pinches, and spreads manipulate screen elements in an intuitive way. Styuses facilitate precision input for drawing, writing, selecting small interface elements, and more.

Output Device Function of Computer
While input feeds information into a computer, output devices present it back to the user in meaningful ways. Output enables seeing results, data representations, system information, digital creations, and more.
– Monitor
The monitor displays graphical outputs like the user interface, images, video, charts, documents, gaming visuals, and other visual information. High resolution and color depth enable clear and vibrant visuals. Size, aspect ratio, refresh rate, response time, and other factors affect how well a monitor outputs all kinds of visual digital information from a computer.
– Printer
Printers facilitate hard copy physical output of digital documents, photos, and more onto paper. Different types like inkjet, laser, thermal, and dot matrix printers work in various ways to mark the pages. Print quality factors like dots per inch and print speed determine printer output functionality. Beyond text documents, printers can output photos, posters, labels, and much more.
– Speakers
Speakers convert electric signals into audio output like music, voice recordings, system sounds, voice calls, media audio, game sounds, and other digitized sounds. Audio fidelity relies on speaker cone size, power, directionality, frequency response range, distortion rate, and more specifications. Multiple speakers can output directional sound. Subwoofers provide deeper bass notes.
– Haptics
Haptic feedback recreates the sense of touch for more immersive computing experiences for entertainment, accessibility, or productivity goals. Vibrating controllers, gloves, seats, and more output touch sensations synchronized with on-screen actions. Force feedback joysticks resist user motions to simulate control of virtual objects. Advanced haptics stimulates tactile receptors to mimic textures, shapes, movements, temperatures, and more.
– Lighting
Lighting elements directly integrated into keyboards, computer cases, monitors, and other devices provide visual notifications and feedback from the system. Colorful Animations, patterns, and effects create aesthetically pleasing outputs that communicate certain information types or just for ambient decoration. Dynamic lighting programmed to react to music, games, incoming messages, and other outputs takes this function even further.
Storage Device Function of Computer
Storage in a computer fulfills the vital function of saving data, programs, files, media, operating systems, settings, and all other information digitally. Saved data stays intact even when powered down, unlike volatile RAM that gets regularly wiped clean. Modern computers utilize several types of storage options that serve key functions:
– Hard Disk Drives
HDDs save and read magnetically encoded data on quickly spinning metal platters inside protective casings. High-capacity hard drives store huge amounts of programs, files, operating systems, and media internally or externally. HDD arrays provide mass amounts of storage to enterprise data centers. Individual users can store entire music, photos, videos, and document collections on them.
– Solid State Drives
SSDs provide faster data access speeds than HDDs for better system performance thanks to integrated circuits saving data electronically instead of magnetic encodings. High-performance computers utilize speedy SSDs for boot drives to launch operating systems and programs rapidly. External SSDs also offer quick data transfer rates and robust portability for storage and transfer needs.
– USB Flash Drives
Small, lightweight, and external USB flash drives offer highly portable storage that fits in a pocket for easy transport. While capacities are typically relatively low, speeds can reach up to USB 3.2 gen 2×2’s 20Gbps for quick data transfers. Encryption keeps sensitive data secure in transit. No moving parts allow use in harsher environments than HDDs.
– Memory Cards
Tiny memory cards serve as primary storage for digital cameras, mobile devices, handheld game systems, drones, and more devices without large internal drives. Speed ratings reaching up to UHS-III facilitate recording High-resolution photos and video. Adapters make pulling data from cards easier on devices with SD slots or by using external USB card readers.
– Optical Discs
CDs, DVDs, and Blu-Ray discs encode data as microscopic pits and lands arranged in spiral tracks molded into layers of polycarbonate plastic. Lasers precisely focus beams to reflect back into sensors revealing the binary data burned into each pit or land. These disc drives offer large, inexpensive storage options for mass-producing media, software, and backups.
– Cloud Storage
Cloud-based storage saves data on remote servers accessible online instead of local drives. This facilitates anytime access to files across devices with internet connectivity. Cloud backup protects data loss in case of disasters damaging local storage. Large-capacity enterprise cloud infrastructure offers businesses scalable storage resources delivered securely over networks.
Processing Device Function of Computer
Processing devices give computers their problem-solving, calculating, and “thinking” capacities. The CPU serves as the key processing unit defining overall computer performance and capabilities. Several supporting components also provide vital processing functions.
– Central Processing Unit
The CPUor processor lies at the heart of any computer system as its main processing chip. Modern CPUs contain multiple processor cores each with cache memory enabling parallel multitasking operations. Powerful CPUs crunch data faster allowing computers to carry out taxing tasks like gaming, video editing, data analysis, 3D modeling, and running intensive creative programs. Upgrading older CPUs provides a major performance boost.
– Graphics Processing Unit
Dedicated GPUs specialize in rendering all kinds of digital graphics instead of depending on the main CPU alone. Massive parallel processing power accelerates tasks like game visuals, VR environments, 3D renderings, video effects, image filters, and neural network training. High-end discrete GPUs greatly increase gaming frame rates and creative workload speeds via added stream processors and abundant VRAM.
– Motherboard
The main printed circuit motherboard facilitates communication between crucial computer components via traces, sockets, interfaces, controllers, and pre-installed processing chips. The chipset in particular manages data flows between storage, memory, expansion slots, networking ports, and the power delivery system. Modern boards provide platforms supporting the latest high-speed connections.
– Co-Processors
Co-processors provide specialized processing capabilities to handle workloads inefficiently processed by main CPUs. Math co-processors offer hardware acceleration for complex calculations. Cryptographic and tensor processing units speed up encryption/decryption and AI workloads. Ray tracing cores support complex real-time 3D rendering. Physics and audio co-processing also assist with specialized tasks.
Conclusion
The four key functions of input, processing, output, and storage all work together to make computers so useful for a vast range of home, business, industrial, scientific, and entertainment applications. Ongoing technological advancement enhances these core functions for ever more powerful and capable machines meeting more demands and use cases than ever before imagined since their inception.
When broken down into constituent devices, the specifics of how these functions operate reveal the incredible ingenuity of computer engineering. Each component plays a crucial role in manipulating and communicating digital data. Computers appear mystifying as integrated systems but make perfect sense when their functional parts are more closely examined.
Understanding what tasks each device handles provides greater insight into choosing optimal computer setups for particular needs. Custom building systems allow tailoring machines by selecting components that excel at certain functions whether that involves maximizing gaming speeds, professional media editing workflows, industrial automation, scientific calculations, enterprise databases, and everything in between.
Knowing the functional roles of these devices also helps when troubleshooting computer problems. Pinpointing exactly which piece may be causing issues makes repairs simpler without having to guess. Future computer breakthroughs surely involve improving upon or even reimagining these core input, output, processing, and storage functions. But all computers whether futuristic or outdated share these same vital purposes. Without anyone, even the most advanced computer gets relegated to nothing more than an inert sculpture.
Now, understanding this concept is simple and entertaining on Hasons. By using Hasons website you can always stay one step ahead in your job, business or studies by purchasing New Age Desktops and All in One Desktops, i3 Intel Core Processor Desktop starting from 15000/-. Monitors, CPUs, Gaming Desktop are also available. Register on Hasons and order your Tech Partner Now. Get exciting offers and benefits on your every purchase. Contact us so our support team will guide you in purchasing your right Tech Partner.
 Gaming PC Core i5 12th Generation | 4gb Graphic Card With Cooling Fan | 8gb RAM | SSD 256 | RGB Keyboard and Mouse | 21.5 Inch Big Screen | Hasons Desktop Set
Gaming PC Core i5 12th Generation | 4gb Graphic Card With Cooling Fan | 8gb RAM | SSD 256 | RGB Keyboard and Mouse | 21.5 Inch Big Screen | Hasons Desktop Set
Call 9766122859 to place an offline order and receive FLAT 500/- DISCOUNT
Rs .48,023.00 only Shop Now!
Function of Computer
- What are the 5 functions of a computer?The 5 key functions of a computer are:
- Input - Entering data and instructions into the computer
- Storage - Saving data, programs and documents
- Processing - Performing calculations and operations on inputted data
- Output - Displaying processed information to the user
- Control - Coordinating hardware components to properly execute input, processing, output and storage tasks
- What is computer by function?A computer is an electronic machine designed and built to perform four key functions – taking inputted data, storing and processing that data through calculations according to defined instructions, and outputting the results back to the user or external devices. Computers receive digital inputs and manipulate them mathematically on a massive scale to produce all kinds of useful outputs.
- What are the main functions of computer science?The four main functions of computer science involve programming, networking, security, and data management. Programming gives computers instructions through coding languages to execute tasks. Networking allows linking computers to share information. Security protects systems against threats like hacking and viruses. Data management facilitates storing, organizing and accessing large amounts of information.
- What is the function and structure of a computer?The structure of a computer comprises integrated circuits, circuit boards, interfaces, buses, cables, cases, and power sources. This hardware structure facilitates the four core functions: input of data through devices like keyboards, processing via the CPU and memory to perform operations and calculations, storage on long term media like hard drives, and output of information back to the user visually, audibly or tangibly.
- What are the 6 functions of a computer?The 6 major functions of modern computer systems are:
- Accept data via input devices
- Store data for ongoing use
- Process data via technologies like CPUs and GPUs
- Output processed information to users
- Network with other systems to send, receive and share data
- Automate tasks through programming
