Difference Between LAN, WAN & MAN
We’ll try to give you Better information about Different between LAN MAN and WAN in this blog.
Local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs) and metropolitan area networks (MANs) are three major types of network systems used in information technology. LAN is a network that typically links a limited number of computers within a specific geographic area. On the other hand, MAN is a broader network that encompasses extensive regions such as towns, cities, and more. The WAN network, however, extends even further, covering vast localities and possessing the capability to interconnect multiple countries. On the surface they may seem similar – after all, they all connect computers and devices together. However, there are important technical, functional and geographical differences between them.
This in-depth blog post will clarify exactly what LAN, WAN and MAN are, provide definitions and examples of each, and compare and contrast the key elements that distinguish them.
What is LAN ?
A local area network (LAN) is a Network that connects computers and devices within a close geographic area such as a home, office building, school or small cluster of nearby buildings.

Here is a more formal definition:
A local area network (LAN) is a network that connects Computers and devices within a limited geographical area such as a home, office building or small group of buildings. LANs allow users to share resources and information with one another. They are owned, operated and used by a single organization.
Some key characteristics of LANs:
- Limited geographic range – Typically a single building or localized cluster of buildings.
- High transmission speeds – LANs can enable very rapid data transfer via technologies like Ethernet.
- Commonly used network technologies – Ethernet, WiFi, powerline networking.
- Privately owned – LANs are owned, managed and utilized by a single entity rather than shared as a public utility.
Common examples of LANs include connecting the computers in a home network for Internet access sharing, linking devices in an office building, or creating a network for communication across a college campus.
What is a WAN?
In contrast to local area networks, a wide area network (WAN) connects computers and devices across a broad geographic area. Here is a WAN defined formally:

A wide area network (WAN) is a network that spans a large physical distance. WANs connect LANs together across cities, states or even countries. They utilize public telecommunication infrastructure like routers to transmit data.
Some key WAN characteristics:
- Long distances – Can cross metropolitan, regional or even international boundaries.
- Leased telecom connections – WANs lease bandwidth capacity from telecom carriers.
- Slower speeds – Data transfer speeds are generally slower compared to LAN due to geographical distances involved.
- Common technologies – MPLS, ATM, Frame Relay. Internet VPNs are also popular.
- Shared public infrastructure – WAN connections utilize shared telecom and cable carrier networks.
Every time you access a website or use Internet-dependent technology outside of your local network, you are using a WAN. Common WAN examples include corporate Networks linking branch offices across the world, retail chains connecting in-store LANs to central data centers, and mobile/cellular communications infrastructure.
What is a MAN?
A metropolitan area network (MAN) in a way combines elements of both LANs and WANs. A MAN typically spans a physical area larger than a LAN but smaller than a WAN for instance, across a city or collection of nearby towns and suburbs rather than a whole country or continent.
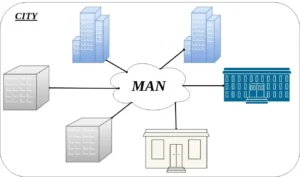
Key MAN characteristics:
- Metropolitan or regional reach – Bigger than a LAN but smaller than a WAN.
- Commonly fiber or wireless-based – Leverages fiber optic cabling and/or wireless transmission.
- Moderately high speeds – Transfer rates faster than WANs but may be slower than LANs.
- Public or private – Some MANs are privately-owned by one entity while others are public carrier networks.
MANs are often set up by entities like universities to connect facilities across a metropolitan zone, or by carriers to connect data or cellular networks throughout a region. MANs play an important “middle” role in networking hierarchy between localized LANs and expansive global WANs.
Now, understanding this concept is simple and entertaining for Hasons. Using the Hason website you can always stay one step ahead in your job, business, or studies by purchasing New Age Desktops and i3 Intel Core Processor Desktop starting from 15000/-. Monitors, CPUs, and Gaming Desktop are also available. Register on Hasons and order your Tech Partner Now. Get exciting offers and benefits on your every purchase. Contact us so our support team can guide you in purchasing the right Tech Partner.
I7 Elite Desktop
Core I7 Desktop Processor Gen 10700/ Chipset Series H510 (Windows 11 Pro/1TB HDD/DDR4-8GB /Wired Keyboard, Mouse/ Black), Screen 21.5
SHOP NOW
Key Differences Between LANs, WANs and MANs
Now that we have defined each type of network, let’s clearly summarize and compare some of the main differentiators:
Network Size and Geography
- LAN – Local area network restricted to small nearby zone like a room, building or cluster of structures.
- MAN – Covers the area of a town, suburb or city including between multiple locations.
- WAN – Wide area network spanning a large geographical zone, even crossing countries and continents.
Data Transmission Speeds
- LAN – Very high speeds. Modern LAN tech like Gigabit Ethernet offers rapid data transfer over limited distances.
- MAN – Moderately high speeds better than WANs. May enable hundreds of megabits to gigabits per second.
- WAN – Generally slower speeds across longest distances. But some forms like 5G are enhancing capacity.
Infrastructure and Technologies
LAN – Uses private cabling like Ethernet and WiFi rather than telecom carrier networks. MAN – May leverage private fiber networks or public metropolitan infrastructure. Uses high bandwidth cable and wireless tech.
- WAN – Depends on wide reach of telecom provider backbone networks like MPLS or Internet infrastructure. Uses longest range technologies.
Network Ownership and Access
- LAN – Privately owned by an individual or single organization. Not accessible to general public.
- MAN – Can be public carrier networks or privately run. Access may be limited.
- WAN – Utilizes shared public infrastructure from telecom and cable companies. Openly accessible but fees often apply.
Primary Users
- LAN – Used by the owner, typically an individual (home LAN) or private company (business LAN).
- MAN – Users are often affiliated somewhat with the owning entity for access. More private than WANs.
- WAN – Very broad usage as people utilize WANs constantly across global personal, work and mobile computing. Most openly accessible of the network types.
Applications of WANs
Since WANs allow communications across long distances, they have all sorts of useful Applications in our modern world:
- Businesses use them to coordinate between branch offices, partners, and employees working remotely
- They allow things like videoconferences, data sharing, email and more on a global scale
- Governments and militaries rely on WANs for command and control operations
- Scientists use them to transfer huge research datasets around the world
- Banking networks, air travel systems, and other critical infrastructures run on WANs
Basically, WANs make it possible for the entire world to be connected, which is pretty amazing when you think about it. From buying things online to checking social media from the other side of the planet, WANs make global communication possible.
Key Initiatives in India for Types of Networks
Here in India, we have some major initiatives to expand and improve network access for people across the country:
NaWAN: This is India’s National Wide Area Network designed to link up government offices, schools, businesses, and service providers on a unified platform.
BharatNet: This huge project aims to provide affordable broadband connectivity via optical fiber to all 250,000+ gram panchayats (village councils).
Smart Cities Mission: Cities across India are working to develop smart, integrated networks and services like traffic management and utilities through MANs.
Digital India: This visionary campaign promotes expanding digital infrastructure like networks to remote areas and improving digital literacy nationwide.
Public Data Offices: Efforts are underway to establish a network of public offices with affordable internet and digital services access for all citizens.
So from rural villages to major metro areas, Indian government and businesses are investing heavily in modern network solutions to empower communities.
Conclusion
In closing, clearly differentiating localized LANs, metropolitan MANs and wide-reach WANs is important for effective network deployment, management, security and usage. Knowing these key contrasts enables much more informed decision making regarding network design, needed capabilities, infrastructure variables, access controls and related elements.
While network categories have blurred somewhat over time thanks to advancing virtualization and wireless equipment, the core tenets separating LANs, MANs and WANs remain largely intact. Each network variety serves important interconnectivity roles powering critical Communication and data accessibility that underpins countless aspects of modern business operations and everyday life.
| If you are reading Difference Between LAN WAN & MAN then also check our other blogs: | |
| Liquid Crystal Display | Types of Virtual Reality |
| DDR3 VS DDR4 | Storage Device |
Difference Between LAN, WAN & MAN
- What are the 3 types of Wi-Fi?The 3 types of Wi-Fi are 802.11a, 802.11b, and 802.11g. The standards differ in frequency bands and maximum bandwidth.
- What is the difference between LAN WAN and MAN Brainly?The key differences are that LANs connect devices in a small local area, WANs connect networks across a large geographic distance, and MANs connect local networks across a metropolitan region or city. LANs are privately-owned, WANs rely on public infrastructure, and MANs can be public or private.
- What are the 4 types of networks?The 4 major types of computer networks are LANs, WANs, MANs, and PANs (personal area networks). LANs serve a small local area, WANs span a broad geography, MANs cover a metropolitan zone, and PANs interconnect personal devices.
- What is an example of a LAN and a WAN?A home WiFi network connecting phones, laptops and smart home devices is an example of a LAN. The Internet itself reaching globally is an example of a WAN.
- Is WiFi a LAN or WAN?WiFi is considered a LAN technology because it provides networking capability within a small local area like a home, office or coffee shop rather than over a wide geography.

