Applications of GPS
Global Positioning System (GPS) technology has become an integral part of our daily lives. From navigation apps on our smartphones to tracking wildlife movements to helping self-driving cars know where they are, GPS now plays a role in many industries and activities. In this blog post, we’ll provide an overview of some of the key applications of GPS technology today.
What is GPS?
GPS stands for Global Positioning System. It is a Network of satellites orbiting the Earth that continuously transmit coded information. GPS receivers on the ground or in the air pick up these signals to determine their precise location, speed, time, and direction.
The concept behind GPS is trilateration. The satellites act like reference points and the GPS device measures the distance between itself and three or more satellites by calculating time delays. It determines its relative position on Earth through geometry and trigonometry principles.
Applications of GPS
Some of the key applications and uses of GPS technology today include:
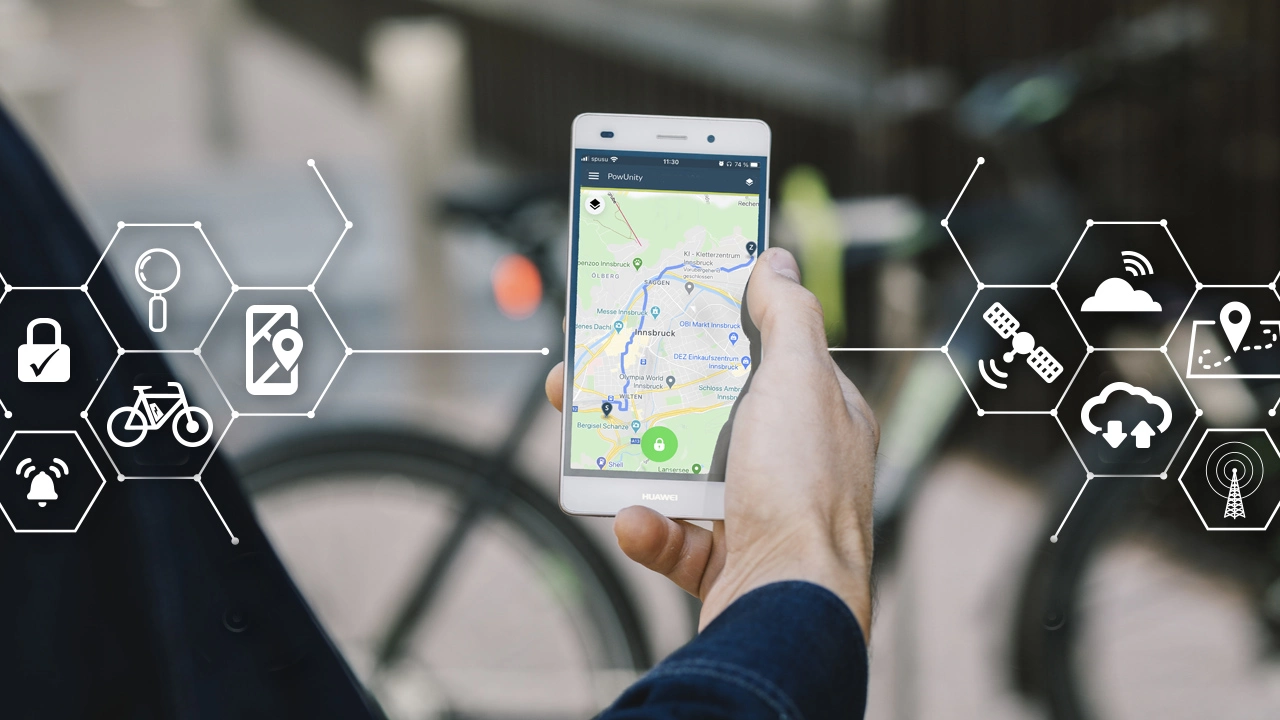
Navigation and Route Planning
Perhaps the most common use of GPS is in navigation and routing. GPS navigation devices and map apps on smartphones use GPS to determine a location and provide directions to destinations. GPS navigation provides real-time traffic updates and rerouting capabilities. This application has transformed how we travel and get from Point A to Point B.
Wildlife Monitoring and Conservation
GPS tracking collars placed on animals allow conservationists to remotely monitor wildlife movements, migrations, habitats, and behaviors. This helps protect endangered species and manages wildlife populations more effectively. GPS gives insights that are near impossible to gain through manual tracking alone.
Precision Agriculture
GPS enables precision agriculture through accurate field mapping, soil sampling, crop spraying, and farm vehicle tracking. By providing precise locations in the field, GPS helps farmers optimize crop yields. They can save costs on seeds, water, pesticides, and fertilizers.
Emergency Services
First responders like firefighters use GPS to rapidly respond to emergency calls and navigate to locations. GPS on ambulances allows dispatch operators to track their movement and send the nearest one in case of a medical emergency. It saves critical time when every second counts.
Fleet Management and Vehicle Tracking
Bus companies, delivery services, trucking companies use GPS for fleet management. GPS tracking systems on vehicles provide real-time locations, fuel usage, idling time alerts, and optimized routes to save costs. GPS helps schedule planned maintenance and diagnostics timely.
Sports and Fitness Tracking
GPS tracking through wearables like smartwatches and fitness bands allows users to precisely track exercise routes, speed, distance covered, elevation gain and other workout metrics. Apps sync the data for analysis. It motivates people to stay fit.
Augmented Reality (AR) Experiences
AR apps leverage GPS, compass, accelerometer data from smartphones to overlay digital information onto the real environment. It offers immersive experiences like interactive tours, visual directions overlays, educational content at heritage sites etc. The possibilities with this technology are immense.
Asset Tracking and Management
High-value assets like containers, construction equipment, rental cars etc. are tagged with GPS trackers. It allows companies to have real-time visibility on the location and movement of assets. GPS helps utilize assets optimally, cuts rental costs and prevents thefts.
Weather Forecasting and Climate Research
Meteorologists use GPS satellite data of atmospheric conditions to forecast weather and track climate changes. The radio occultation technique uses GPS to measure atmospheric parameters critical for numerical prediction models. This leads to more accurate weather prediction.
Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving vehicles rely extensively on GPS and supplemented sensors to know their precise location at all times. GPS tells them the road network and relative position to navigate independently. However, GPS alone is not adequate for autonomous vehicles.
Maritime Navigation and Safety
GPS receivers are ubiquitous on ships, boats, ferries and play an important role in maritime navigation. It serves as an accurate time-space-position information system at sea, provides critical navigation data and augment safety. GPS is a back-up system to radars.
Now, understanding this concept is simple and entertaining for Hasons. Using the Hason website you can always stay one step ahead in your job, business, or studies by purchasing New Age Desktops and All in One Desktops, i3 Intel Core Processor Desktop starting from 15000/-. Monitors, CPUs, and Gaming Desktop are also available. Register on Hasons and order your Tech Partner Now. Get exciting offers and benefits on your every purchase. Contact us so our support team can guide you in purchasing the right Tech Partner.
UltraPulse Ultimate Desktop
I7 All In One Desktop With Processor Gen I7 12700 /Chipset Series Q670 Windows 10 Pro, 512 SSD, DDR4-8GB, Wired Keyboard Mouse, Black Screen 23.8
Shop Now
Working of GPS
GPS works through a concept called trilateration. GPS satellites continuously transmit radio signals that carry timestamps. The ground receivers pick up signals from a minimum of 3 satellites to determine the user location and time offset from the satellite time.

More the number of satellites visible to the receiver, the better is the location accuracy. The receiver measures tiny time offsets to calculate distance from satellites through signal travel time. Based on distance from multiple satellites, the intersection point of spheres is the precise location.
Advanced receivers use augmentation systems like Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS) to correct any errors and achieve higher accuracy.
Applications of GPS – Conclusion
As seen above, Global Positioning System or GPS technology has become deeply embedded in our daily lives. From simple navigation to complex autonomous vehicles, GPS provides the vital function of knowing precisely where you are on planet Earth.
Governments, private companies and civilians benefit tremendously from the wide gamut of applications that GPS has enabled over the past few decades. And with smartphones bringing GPS receivers in our pockets, this utility will continue to grow leaps and bounds.
| For updates in the Application of GPS, read Hasons Blogs. | |
| Trading Monitor | Secondary Storage Devices of Computer |
| India’s first Supercomputer | Magnetic storage Device |
Application of GPS
- What are the 5 GPS applications?Navigation, tracking, mapping, augmented reality experiences, emergency services.
- What are the application and function of GPS?Some key functions include providing precise location data, navigation and routing, tracking vehicles and assets, guiding autonomous vehicles, mapping and surveying, augmented reality, emergency assistance, etc.
- What are the applications of GPS Wikipedia?As per Wikipedia, key GPS applications are in navigation, positioning systems, tracking vehicles and shipment, cell phone and wireless assist, augmented reality experiences, cartography and land surveying, precision agriculture practices, timing and synchronization of computer networks, weather forecasting and hurricane hunting.

