Wireless Network
What is Wireless Network? – In Wireless networks have become the backbone of communication infrastructure in modern society with today’s global interconnectivity. We use wireless connectivity from the internet on smartphones to streaming a movie on smart TVs. But before we look at how and where you can use a wireless network and compare it to a network? Well, let’s go deep and learn more about wireless networks.
What is a Wi-Fi or Wireless Network vs a wired network?
Wi-Fi is a type of network technology that designs methods for the communication of devices without the use of cables for internet connectivity. This is different from wired networks that use Ethernet cables to connect devices in the network. The Wireless Networks are slightly more flexible in terms of usage since no physical cables restrict users’ mobility within the range of the established network.
A wireless connects devices without cables which enable it to move from one point to the other. While the wireless network is where devices such as computers, scanners, and POS machines connect using wireless technology, the wired network is where these devices connect using cables.

There are more subtle differences: Current wired networks are said to be ‘full-duplex’ as they are capable of transmitting and receiving information at the same time. Often each unit has its wire or these cables can be connected in parallel.
Wireless LANs use radio frequencies, which are transmitted by various users and other devices simultaneously. Unlike wired networks, Wi-Fi comes in only “half-duplex”, i. e. , it can transmit or receive data at any given time. Cohorts interact taking turns to use the space for conveying information. Furthermore, all other people in the network can monitor the data being transmitted across the network. To achieve privacy, Wi-Fi networks employ various measures of security.
What are the benefits of a Wi-Fi wireless network?
There are several advantages associated with the use of a Wi-Fi wireless network.
- Flexibility Applications: The use of the network is flexible since users can access it from any point of coverage.
- Convenience: Cordless, so it is very convenient to connect and, as a result, combine various devices.
- Scalability: Another feature, that can be distinguished, is that wireless networks are easily scalable to handle more devices
- Cost-effective: Saves on the expenses of having to install costly cables and wires throughout various establishments.
Types of Wireless Network Connections
These include a personal-area network (PAN), a metropolitan area network (MAN), and a wide-area network (WAN).
LAN
A Local Area Network is a computer network that is contained within a single geographical region, like in an office complex. It can link many numbers of elements wherein the examples are computers, printers, as well as data storage devices. LAN elements include switches, access points, routers, firewalls among others, and the Ethernet cables that provide the connection. Wireless LAN is mainly known via Wi-Fi.
PAN
Personal-area network is a network crafted around an individual’s devices in a given environment or location. A PAN could allow having computers, telephone sets, and video games among other peripheral devices. These are particularly found within residential premises as well as in small commercial properties. Of the different wireless PANs, Bluetooth is the most famous one.
MAN
Metropolitan-area network is a computer network favored in a city, small geographical area or business or college campus. There is one primary characteristic that sets a MAN from a LAN; size. A LAN most often occurs as a single-building or single-area installation. Most organizations can be covered by a man within several square miles depending on the availability of his services.
For instance, large firms may find a need to incorporate a MAN if the firm occupies a large space of land and has elements such as air conditioning and electricity which have to be monitored from one central point.
WAN
A wide-area network WAN will then be one that will cover a very large area, perhaps an entire city, state, or country. The Internet is a WAN-Wide Area Network. Similar to the internet a WAN can have other subnets, LAN or MAN. The most familiar wireless WANs are what we popularly refer to as cellular services.
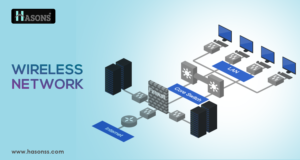
The components of a wireless network
Wireless Router: The central hub that connects all devices to the network and allows data transmission.
Wireless Network Interface Card (NIC): Installed in devices to enable wireless communication with the router.
SSID (Service Set Identifier): The unique name of the wireless network that devices connect to.
Encryption: Security protocols like WPA, WEP, or WPA2 protect data transmitted over the network.
Access Point: Extends the range of the network by boosting the Wi-Fi signal in hard-to-reach areas
Wi-Fi connection network modes
Sure, here’s a simplified and point-wise version: Sure, here’s a simplified and point-wise version
Infrastructure Mode:
- Most are usually found in homes or business premises in areas such as desks, tables, and even computers.
- Needs a device to connect to, like a router, for other devices to connect with it.
- An access point controls connections and gains connection to the internet as well as to other devices.
Ad hoc Mode:
- Sometimes referred to as P2P mode as well.
- Devices in a link are able to communicate with one another without any form of intermediary known as an access point.
- Especially beneficial in communicating between devices that are proximal to each other.
Wi-Fi Direct:
- A special mode of wireless LANs that has features similar to ad hoc mode but also offers extra capabilities.
- Enables devices to join that do not have an access point.
- P2P is commonly employed where devices require exchanging information such as files or even playing streaming content directly on target devices (for example, between a telephone and a television set).
Wi-Fi Hotspot
- Normally seen at grounds near cafes, airports, or bus terminals.
- Dials up an Internet connection to give connection to the users without needing to enter login details (some may be charged).
- Some of the features of modern smartphones include the capability of providing internet connection for other devices, that is; this function guards its connection securely.
Conclusion
What is Wireless network have revolutionized the way we connect to the internet, providing us with greater flexibility and convenience. By understanding the benefits, deployment process, types of connections, also components of wireless networks, you can make the most of your wireless experience.
| If you are reading What is Wireless Network then also check our other blogs: | |
| Web Technology | Data Transmission |
| Components of computer network | Types of scanner |
Wireless Network
- What is a wireless network?A wireless network allows devices to connect to the internet without physical cables, providing flexibility and convenience.
- What are the different types of wireless networks?Types of wireless networks include Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular networks, each serving different connectivity needs.
- How can I secure my wireless network?Secure your network by setting a strong password, enabling encryption, and limiting access to authorized devices.
- What factors can affect the performance of a wireless network?Interference from other devices, distance from the router, and network congestion can affect the performance of a wireless network.
